Yo, Gengs I'm back again. So, at this time I will give you a last lesson in semester 3. It's about explanation text. Time flies by, right? Please read this last lesson :D
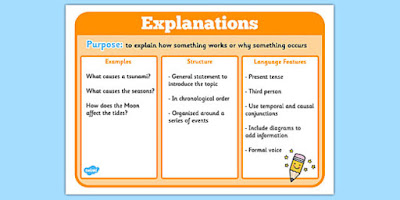
Definition
Explanation text is a text which explains how and why a phenomenon happens. It includes both natural and social phenomena. (https://www.ruangguru.com)
Procedure texts and explanation texts are different in terms of their structure and purpose. Explanation text aims to explain why and how something happened. You can read about procedure text in the link below.
Generic Structure
– General statement
General statement; stating the phenomenon issues which are to be explained.
– Sequenced of explanation
Sequenced explanation; stating a series of steps which explain the phenomena.
—Conclusion
Conclusion; Contains conclusions regarding the topics discussed.
Language Features
1. Explanation text is typically written in the present tense with formal to-the-point language that doesn’t deviate from the topic.
2. It uses separate text with headings and subheadings to make the explanation text simple and easy to understand.
3. Add pictures and diagrams with labels for visual learners.
4. Any technical vocabulary used should fit into a glossary at the end to help with jargon.
5. Numbered points that explain something step-by-step.
Example
The Scientific Method Used at NASA’s
 |
| https://pin.it/4sca3WE |
The scientific method is the gold standard for exploring our natural world. We might have learned about it in grade school, but here’s a quick reminder: It’s the process that scientists use to understand everything from animal behavior to the forces that shape our planet—including climate change.
The exact steps of the scientific method can vary by discipline, but since we have only one Earth (and no “test” Earth), climate scientists follow a few general guidelines to better understand carbon dioxide levels, sea level rise, global temperature and more.
After a hypothesis (a statement that an experiment can test) is formed, observations (experiments and data gathering) are conducted. Conclusions are made after the data is analyzed and interpreted. The results that can be published must be validated with further experiments (rinse and repeat)
The scientific method is iterative (repetitive), meaning that climate scientists are constantly making new discoveries about the world based on the building blocks of scientific knowledge.
Okay, Gengs! That's a last lesson in semester 3. Hope y'all understand about this lesson. Leave any feedback on comment column below!

Komentar